Disc degeneration is one of the most common causes of chronic back pain. It occurs when the intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers between your spine’s vertebrae, begin to deteriorate over time. This condition can lead to discomfort, reduced mobility, and a range of other symptoms that impact your daily life. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available for disc degeneration.
1. What Is Disc Degeneration?
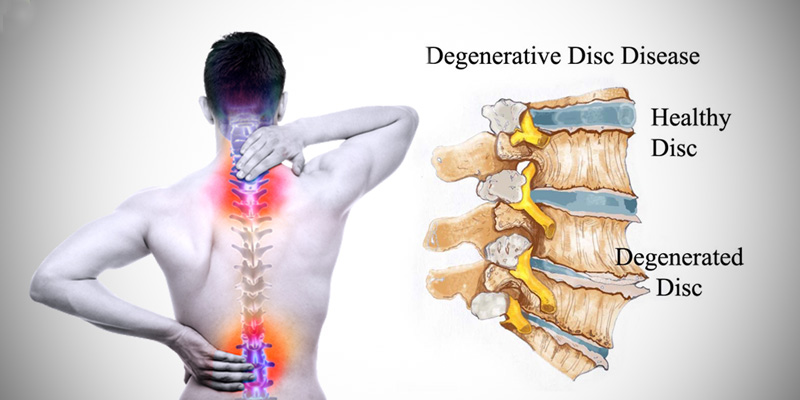
Disc degeneration refers to the gradual breakdown of the intervertebral discs, which are located between the vertebrae in your spine. These discs provide cushioning and allow your spine to move smoothly. Over time, due to wear and tear, the discs may lose their water content, causing them to become less flexible and more prone to damage.
As the discs degenerate, they can lead to conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and other spinal problems, which can cause significant pain and mobility issues.
2. Symptoms of Disc Degeneration
The symptoms of disc degeneration can vary from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the damage. Common symptoms include:
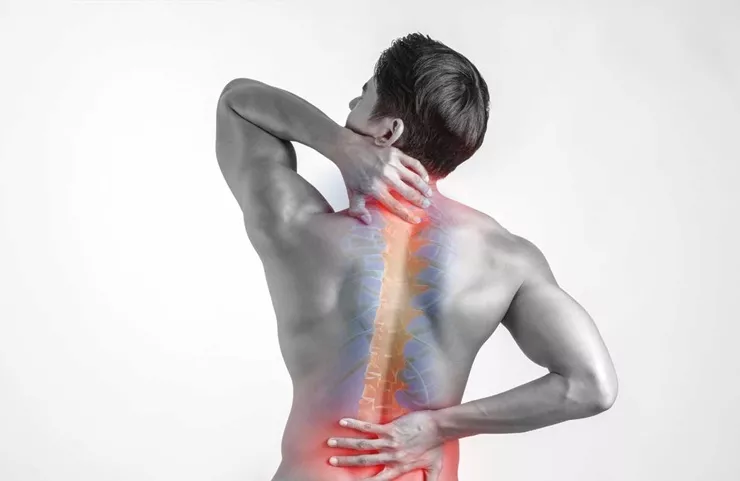
- Chronic Back Pain: The most common symptom of disc degeneration is persistent pain in the lower back, especially when sitting, bending, or lifting.
- Numbness or Tingling: As the disc degeneration progresses, it may put pressure on nearby nerves, leading to numbness or tingling in the legs or arms.
- Weakness in the Limbs: Nerve compression caused by disc degeneration can result in weakness in the arms, legs, or feet, affecting your ability to walk or move.
- Reduced Flexibility: As the disc loses its ability to absorb shock and facilitate movement, you may experience stiffness and reduced flexibility in your spine.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult an orthopedic spine specialist for a thorough evaluation.
3. Causes of Disc Degeneration
While disc degeneration is primarily associated with aging, several factors can accelerate the process or increase the risk of developing the condition:
- Aging: As we age, the discs in our spine naturally lose water content and become less effective at absorbing shock.
- Repetitive Motion or Strain: Jobs or activities that involve repetitive bending, lifting, or twisting can put extra stress on the discs, leading to quicker degeneration.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to early disc degeneration, making them more likely to develop spinal issues at a younger age.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can place additional strain on the spine, leading to faster disc degeneration.
- Previous Injury or Trauma: A past injury to the spine, such as a car accident or fall, can damage the discs and increase the risk of degeneration.
4. Treatment Options for Disc Degeneration
When it comes to treating disc degeneration, options can range from conservative, non-surgical approaches to more advanced treatments, including surgery. The treatment plan will depend on the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, and their overall health.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can help manage inflammation and pain associated with disc degeneration.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, using proper posture, and avoiding activities that strain the back can help reduce symptoms.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: In some cases, injections of corticosteroids can provide temporary relief from inflammation and pain in the affected area.
Surgical Treatment Options:
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, or when disc degeneration leads to nerve compression, surgery may be necessary. Dr. Manojkumar Gaddikeri specializes in advanced spinal procedures, including:
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS): This technique allows for smaller incisions, quicker recovery times, and less pain compared to traditional open surgery.
- Spinal Fusion Surgery: In severe cases of disc degeneration, spinal fusion surgery may be required to stabilize the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae together.
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing the damaged portion of the disc to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
5. Prevention of Disc Degeneration
While you cannot entirely prevent the natural aging process, you can take steps to reduce your risk of early disc degeneration:
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthening your core muscles and maintaining flexibility can help protect your spine.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess weight can take pressure off your spine and reduce the risk of disc degeneration.
- Avoid Poor Posture: Practice good posture when sitting, standing, and lifting to reduce unnecessary strain on your back.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the discs hydrated, which can prevent early degeneration.
Conclusion
Disc degeneration is a common cause of back pain, but with the right treatment and lifestyle modifications, its impact can be minimized. Whether through non-surgical approaches like physical therapy and medications or more advanced options like minimally invasive spine surgery, many effective treatments are available to help you manage the condition and improve your quality of life.